Describe the Function of Schwann Cells
The Schwann cell plays a vital role in maintaining the peripheral nervous system PNS. The conduction of nerve impulses across axons nerve growth and regeneration trophic support for neurons production of the nerve extracellular matrix regulation of neuromuscular synaptic function and.

Schwann Cells Video Organ Systems Khan Academy
The Schwann cells do not degenerate.

. When motor neurons are severed causing nerve terminals to degenerate Schwann. Schwann cells are derived from the neural crest and play crucial roles in the maintenance and regeneration of the motor and sensory neurons of the. The neurilemma assists in regeneration of an axon when it is damaged by forming a regeneration tube to stimulate and guide its regeneration.
They also secrete proteins such as laminin and collagen and cell adhesion molecules involved in binding with other cells to support the regeneration process. As the neuron recovers its axon grows into the site of injury and then distally along the path created by the newly divided Schwann cells. These cells surround nerves to hold them in place supply neurons with nutrients and oxygen insulate the.
The main function of Schwann cells is to support myelinated and unmyelinated nerve cell fibers. In this sense Schwann cells give rise to so-called saltatory conduction of myelin-containing neurons. Schwann cells are a type of glial cell that surrounds neurons keeping them alive and sometimes covering them with a myelin sheath.
The function of this sheath is to protect and direct the nerve impulses. To form the sheath Schwann cells wrap around a segment of an axon. Schwann cells embryologically derive from the neural crest.
In PNS schwann cells produce a lipid-rich layer called the myelin sheath that surrounds the axons. This insulation is responsible for wrapping the axon and cause an electrical signal that runs without losing the intensity. Presentation of antigens to T-lymphocytes.
The myelin sheath provides electrical insulation. Schwann cells are derived from neural crest cells and come in two types either myelinating or non-myelinating Schwann cells. Schwann cells make up what is called the myelin sheath around the axon of the neuron.
Schwann cells are part of the peripheral nervous system PNS They have two major functions they produce the myelin sheath which covers the schwan cell which helps to repair and regenerate. The function of this sheath is to protect the axon and direct the nerve impulses facilitates conduction of electrical signal. The Schwann cells increase the amount of growth factors such as neurotrophins which are proteins that increase the survival and function of neurons.
If the myelin sheath that the Schwann cells make up becomes damaged then the impulses cannot. The Schwann cell plays a vital role in maintaining the peripheral nervous system PNS. They function a lot like oligodendrocytes in that they provide myelin sheaths for axons but they exist in the peripheral nervous system PNS rather than the CNS.
Schwann cells make up what is called the myelin sheath around the axon of the neuron. Schwann cells are present in the peripheral nervous system whereas oligodendrocytes are similar cells found in the central nervous system. Number of axons myelinated Oligodendrocytes are capable of myelinating multiple axons at once.
Myelination increases conduction velocity along the axon allowing for the saltatory conduction of impulses1. Describe the function of Schwann cells. Both play a pivotal role in the maintenance and regeneration of axons of the neurons in the PNS.
Over this period macrophages move into the area and remove the degenerating debris distal to the injury site. Schwann cells differentiate from cells of the neural crest during embryonic development and they are stimulated to proliferate by some constituent of the axonal surface. Develop from neural crest cells and differentiate by expressing transcription factor SOX-10.
If the Schwann cells are damaged it can cause a number of motor problems which can include paralysis. However instead of being a central cell with membrane-tipped arms Schwann cells form spirals directly around the. Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS also include satellite cells olfactory ensheathing cells enteric glia and glia that reside at sensory nerve endings such as the Pacinian corpuscleThe two types of Schwann cells are.
Schwann cells myelinate the nerve cells that project to and from our muscles internal organs and the other signals in the peripheral nervous system. Schwann cells are the principle glia which are neuron supports in the peripheral nervous system. Schwann cell functions provide a protective covering delivers material to and removes material from the neuron axon greatly increase the speed of impulse enable repair of PNS neurons.
Schwann cells produce the myelin sheath around the axon in peripheral nervous system. They myelinate peripheral nerves and serve as the primary glial cells of the peripheral nervous system PNS insulating and providing nutrients to axons. Instead they proliferate along the path of the original axon.
The essential role of immature Schwann cells is to act as a pool from which myelin and nonmyelin Remak cells develop while Schwann cells in damaged nerves carry out specific functions related to regeneration and wound repair. Schwann cells also play a role in forming connective tissue sheaths in neuron development and axon regeneration providing chemical and structural support to neurons. By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework questions.
Schwann cells are derived from neural crest cells and come in two types either myelinating or non-myelinating Schwann cells. Both play a pivotal role in the maintenance and regeneration of axons of the neurons in the PNS. Schwann cells act in the peripheral nervous system as electrical insulators through the myelin.
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system PNS. Schwann cells are named for physiologist Theodor Schwann who discovered them. YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE.

Schwann Cells Biology Dictionary
Difference Between Schwann Cell And Oligodendrocyte Definition Characteristics Function

Anatomy Physiology Nervous Tissue Homeostasis Excitable Characteristic Of Nervous Tissue Allows For Generation Of Nerve Impulses Action Potentials Ppt Download

1 2 The Nervous System And Nervous Tissue Neuroscience Canadian 1st Edition Open Textbook

Oligodendrocyte Physiology Britannica

What Is The Role Of Neuron Schwann Cells Quora

Schwann Cells Biology Dictionary

What Is The Function Of Schwann Cells In Unmyelinated Axons Quora
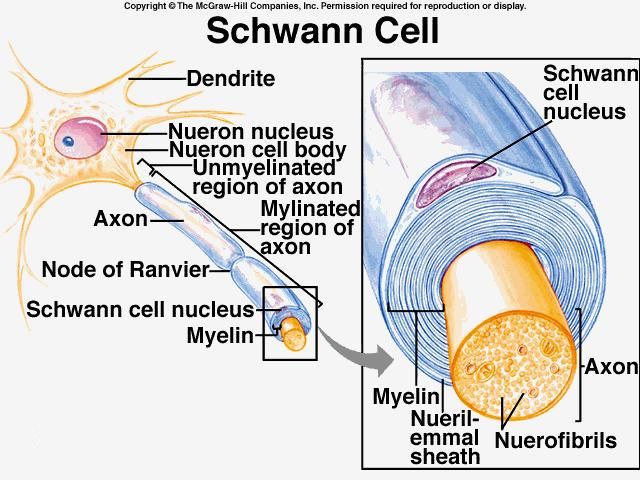
In Human Anatomy What Is The Purpose Of The Schwann Cells Socratic

Schwann Cells Function Simply Psychology
The Nervous System Structure And Function Nursing Part 1

Difference Between Oligodendrocytes And Schwann Cells Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
What Is The Role Of Neuron Schwann Cells Quora

Myelination Of Axons By Schwann Cells

Nodes Of Ranvier Overview Function What Are Nodes Of Ranvier Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

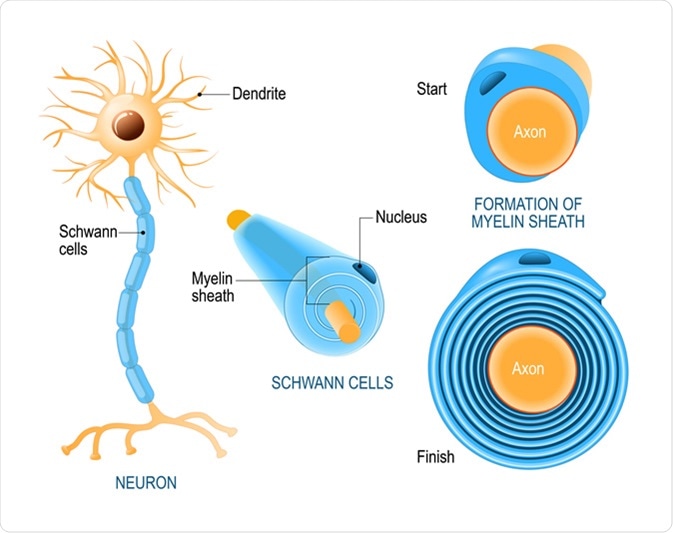
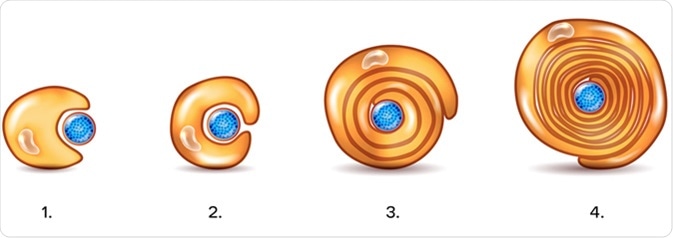
Comments
Post a Comment